Aging is a natural process that everyone experiences as they progress through life.
It is often accompanied by various subtle and gradual changes that can be physical, emotional, and cognitive.
Recognizing these initial signs can help individuals better understand their bodies and adapt to the transitions that come with getting older.
Here, we’ll explore the most common early signs of aging and delve into how they manifest.
1. Changes in Skin and Hair
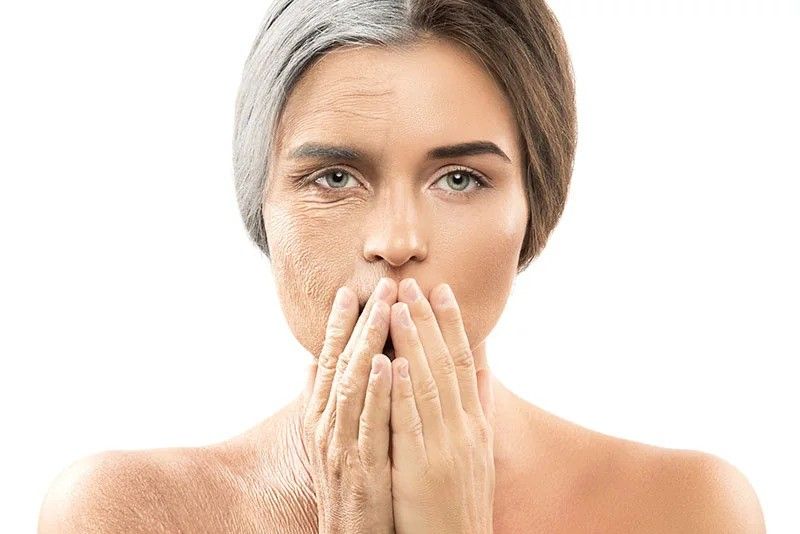

One of the most noticeable signs of aging appears on the skin.
Collagen production begins to slow down as early as the mid-20s, but the effects become more visible by the late 30s or early 40s.
Here are key indicators:
- Fine Lines and Wrinkles: These first appear around the eyes and mouth due to repetitive facial expressions and reduced elasticity.
- Drier Skin: The skin may begin to lose moisture, leading to dryness and a rougher texture.
- Age Spots: Often called liver spots, these are flat, dark areas that develop due to sun exposure over time.
- Thinning Hair: Hair loss or thinning is a common sign, often influenced by genetic factors and hormonal changes.
2. Reduced Energy and Stamina
As people age, they may start to notice a decline in their overall energy levels.
While this doesn’t happen overnight, many individuals report feeling fatigued more easily and needing longer periods of rest after physical activities.
The body’s metabolism also tends to slow down, making it more challenging to maintain energy levels throughout the day.
3. Joint Stiffness and Minor Aches
Joint pain and stiffness can start to become more noticeable with age, often due to the gradual wear and tear on cartilage.
The knees, hips, and fingers are particularly susceptible. This is often one of the first signs that aging is affecting physical mobility.
Though it’s not uncommon for younger adults to experience joint discomfort after intense activity, chronic stiffness that persists could be an early indicator of osteoarthritis or general aging.
Also Read: 12 Age is Just a Number Quotes
4. Changes in Vision and Hearing
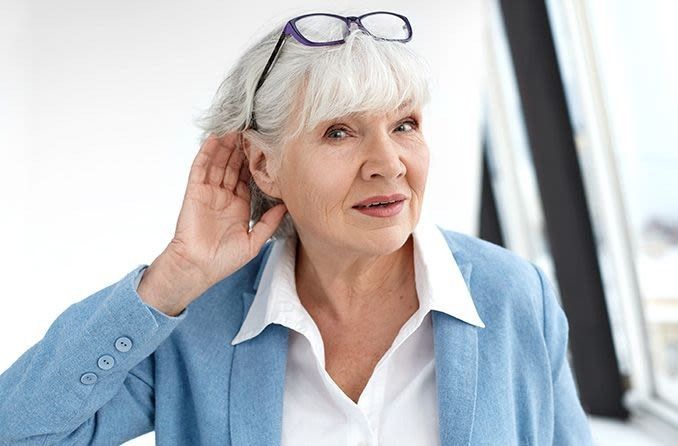

Vision and hearing changes are commonly associated with aging, and they may appear earlier than expected:
- Presbyopia: This is the loss of the ability to focus on close objects, often starting in the early 40s. Reading glasses may become necessary.
- Hearing Loss: Age-related hearing loss, or presbycusis, typically begins with difficulty hearing higher frequencies. Individuals may notice themselves asking others to repeat words more frequently or struggling in noisy environments.
5. Cognitive Shifts
The brain experiences natural changes as we age.
While significant memory loss or confusion can be symptoms of more serious conditions like dementia, minor cognitive shifts are normal:
- Slower Processing Speed: The brain’s ability to process information may slow, leading to longer reaction times.
- Mild Forgetfulness: Occasional lapses, such as forgetting where you left your keys or the name of an acquaintance, are normal early signs of aging.
- Difficulty with Multitasking: Completing multiple tasks simultaneously may become more challenging as mental focus shifts with age.
6. Changes in Sleep Patterns
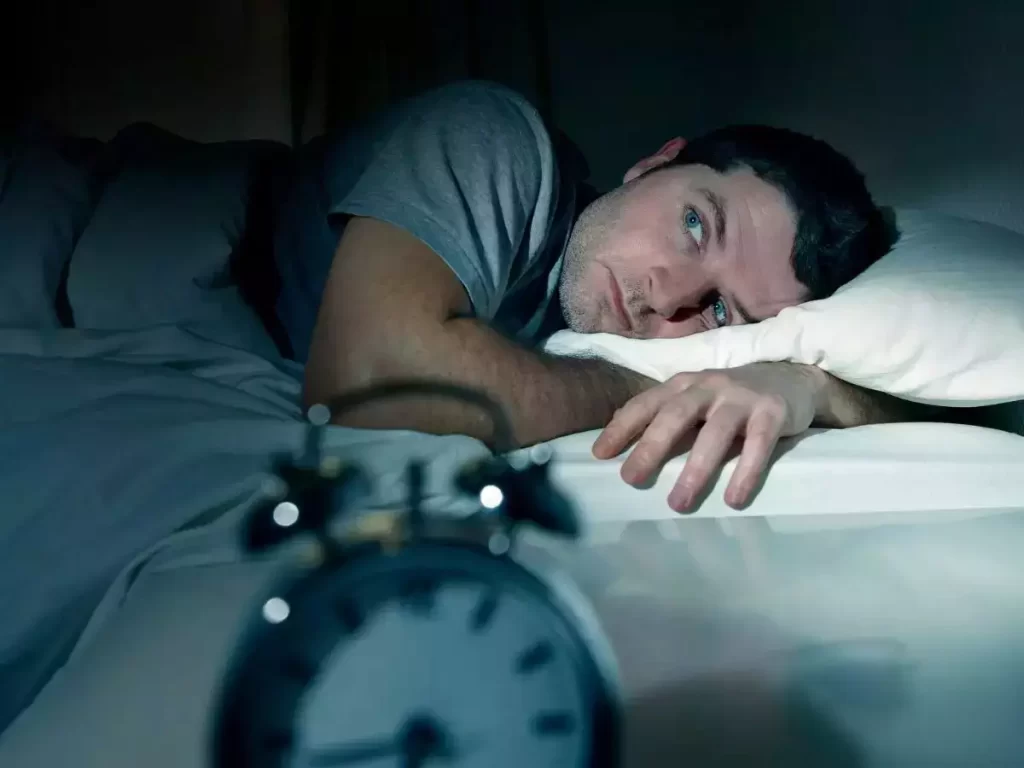

Older adults often report changes in their sleep habits.
It may become more difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep, resulting in less restorative rest.
This change can be attributed to shifts in circadian rhythms and lower production of sleep-promoting hormones like melatonin.
While these changes are normal, chronic sleep disruptions can impact mood and overall well-being.
7. Weight Fluctuations
Metabolism gradually slows down as we age, which can lead to weight gain even without a significant change in diet or physical activity.
Hormonal shifts, such as reduced levels of growth hormone or estrogen, also play a role.
Maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine becomes increasingly important to manage weight effectively and counteract muscle loss.
8. Changes in Muscle Mass and Strength
Sarcopenia, or age-related muscle loss, begins subtly in a person’s 30s and accelerates with age.
This gradual decrease in muscle mass and strength is noticeable in the form of reduced endurance and increased difficulty in performing daily tasks that once seemed easy.
Strength training and regular exercise can help mitigate these effects and preserve muscle function.
9. Dental and Oral Health Changes
Gums may start to recede, and teeth can become more susceptible to decay as the enamel wears down.
This is often an overlooked aspect of aging, but maintaining good oral hygiene becomes even more important to prevent problems such as gum disease and tooth sensitivity.
10. Shifts in Emotional and Mental Well-being
Aging can come with shifts in mood and emotional health.
While many people remain vibrant and fulfilled, some may experience feelings of sadness or mild depression due to lifestyle changes, reduced social interactions, or hormonal fluctuations.
Maintaining a strong support network and engaging in meaningful activities can help counteract these emotional shifts.
See Also: Differences Between Chronological and Biological Age?
11. Decreased Immune Function
The immune system naturally becomes less effective with age, which can lead to an increased susceptibility to common illnesses like colds and flu.
This decline can also result in longer recovery times from minor injuries or infections.
12. Digestive Changes
Some individuals may notice changes in their digestive system, such as slower metabolism leading to bloating or constipation.
This can be linked to a decrease in muscle tone in the digestive tract and changes in gut microbiota composition.
Staying hydrated, maintaining a fiber-rich diet, and regular exercise can help support digestive health.
13. Loss of Flexibility
Flexibility can decline as connective tissues like ligaments and tendons become less elastic.
This can result in reduced range of motion, making activities that require bending or stretching more difficult.
Regular stretching and yoga can be beneficial in preserving flexibility and preventing injuries.
Conclusion
Aging is an inevitable part of life, and recognizing these first signs helps individuals better prepare and adapt to these changes.
While many of these signs can be discouraging, it’s important to remember that aging is a natural process and can be managed with proactive lifestyle choices.
By staying active, eating healthily, nurturing social connections, and maintaining a positive mindset, one can age gracefully and continue to lead a fulfilling life.
Embracing the journey and listening to the body’s signals are key steps in making the most of every stage of life.

Akash Singh is a finance enthusiast who shares valuable insights on various calculators.
